S-function Examples
We provide Simulink examples to demonstrate the BeamNG-Simulink co-simulation in action. To execute these examples effectively, it is crucial to configure the three control parameters described in this document: window width, send wait, and send offset. The examples are available in the models named throttle_example.slx and torques_example.slx, detailed below:
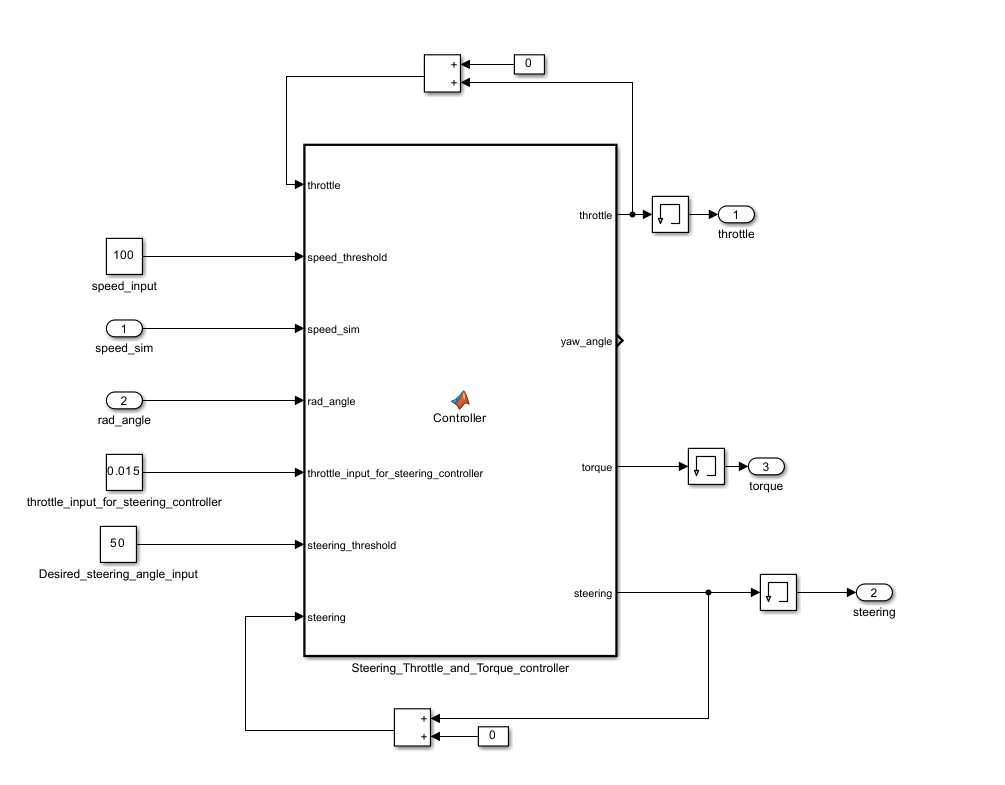 Figure 1: The controller used in both examples
Figure 1: The controller used in both examples
Copy the examples folder to your current working directory, by running the following in the MATLAB command window:
beamng.copy_examples
Both examples are located in examples/simulink/S-function. Change your working directory to this folder.
Example 1: Pedal Control to Maintain Speed Limit
The example throttle_example.slx maintains the vehicle’s speed limit and orientation angle on the map. The block receives vehicle orientation information (yaw angle) and speed as input and controls the vehicle via throttle and steering angle. The speed limit can be adjusted using the speed_input constant block, and the orientation angle with the Desired_steering_angle_input constant block to the controller as shown in Figure 1.
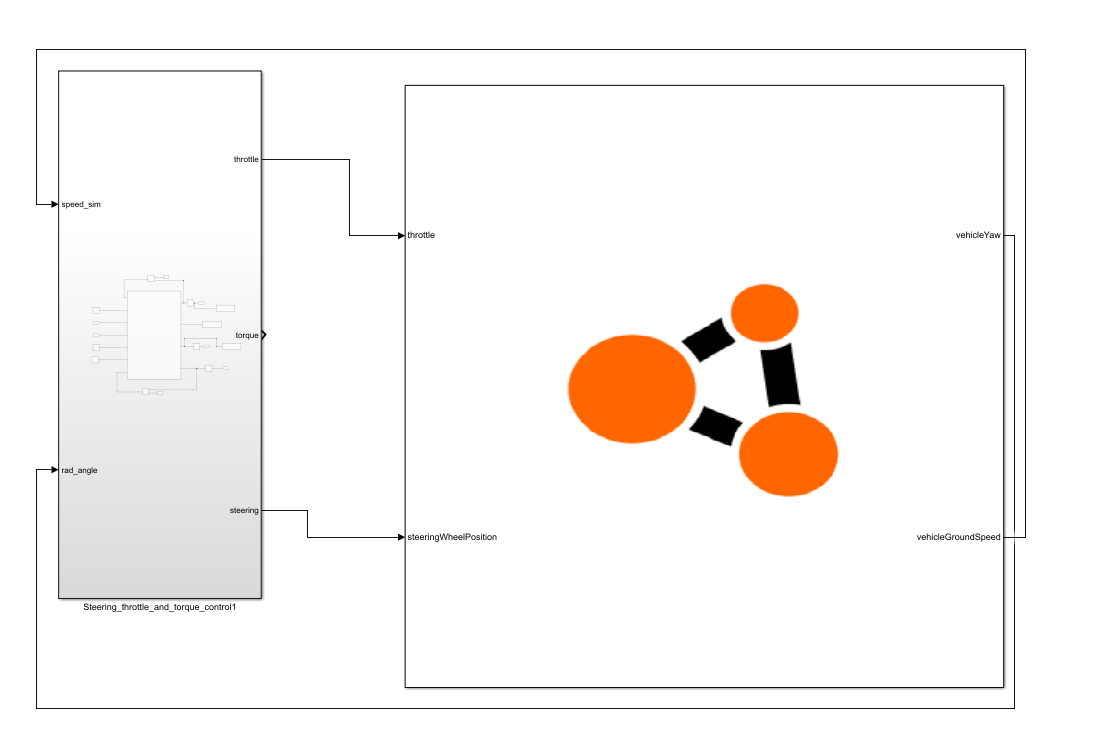 Figure 2: Throttle example
Figure 2: Throttle example
Example 2: Wheel Torques to Maintain Speed Limit
The example torques_example.slx also maintains the vehicle’s speed limit and orientation angle on the map. In this case, the vehicle is controlled through torques applied to each wheel. Adjustments to the speed limit and orientation angle are made in the same way as in the throttle example.
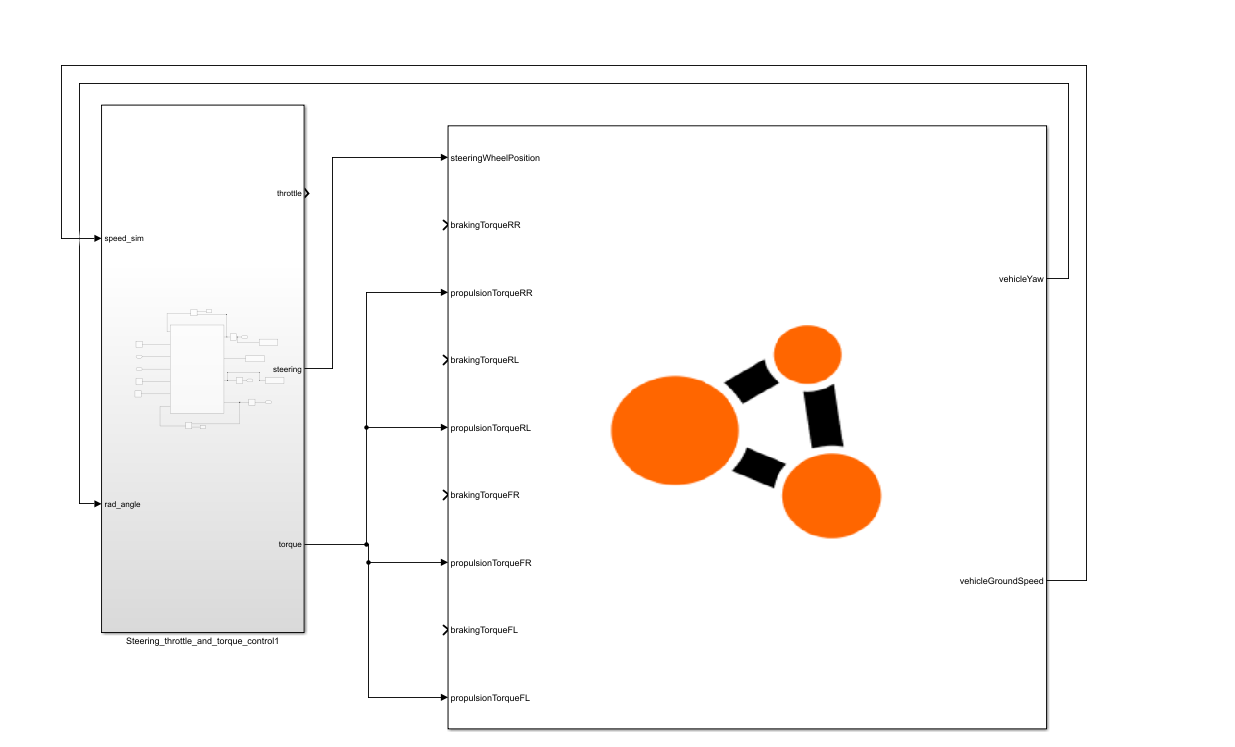 Figure 3: Torques example
Figure 3: Torques example
How to run each example
To run one of above examples, follow these steps:
In MATLAB, change your working directory to
examples/simulink/S-function(runbeamng.copy_examplesif you haven’t done so yet)Launch BeamNG.tech
Click on Freeroam
Select a map, e.g. Grid, Small, Pure and choose a spawn point, click Spawn
The default vehicle will be used, if you want to use another vehicle, press
Escand click on Vehicles or pressCtrl+Eand choose the vehicle you likeNote
The communication interface (csv file) is vehicle-specific, because not all signals are available for all vehicles. These examples, however, use only basic signals available for all vehicles that have a powertrain (but not other objects selectable in the vehicles menu such as a cone).
In the simulation, press
F11to open the World EditorClick on Co-Simulation Editor to open it
Copy both
.csvfiles from your MATLAB working directory toC:\Users\<User>\AppData\Local\BeamNG.drive\<Version>, where<User>is your username and<Version>is the version of BeamNG you are using.In the Co-Simulation Editor, select CoSim from the dropdown menu
Click Start coupling with 3rd party, select the
.csvfile of the example you want to run (e.g.throttle_example.csvfor the throttle example) and click OpenBeamNG will freeze and the window might be still open for a while. This is normal, as it is waiting for Simulink to start the co-simulation.
Open the Simulink model you want to run (e.g.
throttle_example.slxfor the throttle example) and click Run. The co-simulation will start and the vehicle will start driving.The model is configured to run indefinitely. To stop the co-simulation, click on Stop coupling with 3rd party in BeamNG. This will also stop the Simulink model after a short period due to a network timeout.
This concludes running the basic co-simulation examples. You could view the scope signals in Simulink or play with the controller parameters to see how the vehicle behaves.