Camera
Overview
The camera sensor provides image data from customizable perspectives and resolutions. It functions similar to its real-life analogue: the video camera. Users can attach multiple cameras at arbitrary locations to vehicles or the scene. Besides color information, these simulated cameras can be configured to also provide semantic annotation and depth information.
The sensor is available to use from Python API , via the sensors configuration tools and with the Lua console , for which the commands are noted hereafter.
Usage
Camera sensors are exposed to Lua through the sensors extension in the tech folder. Using this API, a Camera sensor can be created with various desired properties, and either attached to a vehicle or to a fixed point on the map.
We can create the Camera either with shared memory or without, using either of the following commands:
sensorId = extensions.tech_sensors.createCamera(vehicleId, args)
sensorId = extensions.tech_sensors.createCameraWithSharedMemory(vehicleId, args)
Args:
- vehicleID(int): The vehicle ID. This can be nil (i.e., 0) if the Camera is not to be attached to any vehicle; this also needs isStatic=true.
The args parameter is a Lua table containing as many of the following properties as required. If any property is not set manually then a default value is used, so it is entirely possible to create the Camera with args being an empty table. What follows is a complete list of these arguments:
-
updateTime(float): How often the Camera sensor should update its readings in the simulator (in seconds). Default value is 0.05.
-
updatePriority(float): A scheduling priority value for this Camera sensor, in range 0 to 1. 0 is highest priority, 1 is least. Default value is 0.0.
-
pos(Point3F): The position of the Camera sensor either in vehicle space (if attached to vehicle) or in world space (if fixed to the map).
-
dir(Point3F): The forward direction in which the Camera sensor points.
-
up(Point3F): The up direction of the Camera sensor.
-
size(Int2): The size of the sensor images.
-
fovY(float): The vertical field of view of the Camera sensor, in degrees. Default value is 70.0.
-
nearFarPlanes(table): The near and far plane distances of the Camera sensor, in metres. * s are {0.05, 100.0}.
-
renderColours(bool): A flag which indicates if colour data should be rendered with this camera, or not. Default value is true.
-
renderAnnotation(bool): A flag which indicates if ‘class’ semantic annotation data should be rendered with this camera, or not. Default value is true.
-
renderInstance(bool): A flag which indicates if ‘instance’ semantic annotation data should be rendered with this camera, or not. Default value is true.
-
renderDepth(bool): A flag which indicates if depth data should be rendered with this camera, or not. Default value is true.
-
isVisualised(bool): A flag which indicates if the camera sensor should be visualised. Default value is true.
-
is_streaming (bool): A flag which indicates whether or not to stream the data directly to shared memory (no poll required, for efficiency).
-
isStatic(bool): True if the camera sensor is fixed to a point on the map, false if it is attached to a vehicle. Default value is false.
-
isSnappingDesired(bool): True if the camera sensor position should be forced onto the surface of the vehicle, at its closest vehicle point. This is useful if finding it hard to have the camera sensor on the vehicle itself. False, otherwise, eg if the camera sensor should be suspended at a fixed point relative to the vehicle. Default value is true.
-
isForceInsideTriangle(bool): Used with isSnappingDesired. True, if the camera sensor should be forced to be inside its nearest vehicle triangle, otherwise false. Default value is true.
-
postprocess_depth (bool): If True, the raw depth data will be postprocessed to better represent values with middle intensity. Defaults to False, as the postprocessing is computationally intensive.
-
is_dir_world_space (bool): Flag which indicates if the direction is provided in world-space coordinates (True), or the default vehicle space (False).
-
integer_depth (bool): If True, depth values will be quantized to the integer range 0-255. If False, depth values will be sent as 32-bit floats in the range of 0.0-1.0. Will be set to False is postprocess_depth=True as full precision is needed for postprocessing. Default value is true.
Returns: sensorId(int): The unique Id number of this sensor, in order to refer to it later, e.g., when closing it.
sensorPosition = extensions.tech_sensors.getCameraSensorPosition(sensorId)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Camera sensor.
Returns: sensorPosition(Point3F) The current position of the Camera sensor, in world space.
sensorDirection = extensions.tech_sensors.getCameraSensorDirection(sensorId)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Camera sensor.
Returns: sensorDirection(Point3F): The current forward direction of the Camera sensor.
sensorUp = extensions.tech_sensors.getCameraSensorUp(sensorId)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Camera sensor.
Returns: sensorDirection(Point3F): The current up direction of the Camera sensor.
maxPendingGpuRequests = extensions.tech_sensors.getCameraMaxPendingGpuRequests(sensorId)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Camera sensor.
Returns: maxPendingGpuRequests(int): The maximum number of pending GPU requests for this Camera sensor.
requestedUpdateTime = extensions.tech_sensors.getCameraRequestedUpdateTime(sensorId)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Camera sensor.
Returns: requestedUpdateTime(float): The current requested update time used by this Camera sensor.
updatePriority = extensions.tech_sensors.getCameraUpdatePriority(sensorId)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Camera sensor.
Returns: updatePriority(float): The current update priority used by this Camera sensor.
extensions.tech_sensors.setCameraSensorPosition(sensorId, pos)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Camera sensor.
pos(Point3F): The new sensor position.
extensions.tech_sensors.setCameraSensorDirection(sensorId, dir)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Camera sensor.
dir(Point3F): The new sensor forward direction.
extensions.tech_sensors.setCameraSensorUp(sensorId, up)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Camera sensor.
up(Point3F): The new sensor up direction.
extensions.tech_sensors.setCameraMaxPendingGpuRequests(sensorId, maxPendingGpuRequests)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Camera sensor.
maxPendingGpuRequests(int): The new maximum number of pending GPU requests for this Camera sensor.
extensions.tech_sensors.setCameraRequestedUpdateTime(sensorId, requestedUpdateTime)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Camera sensor.
requestedUpdateTime(float): The new requested update time for this Camera sensor.
extensions.tech_sensors.setCameraUpdatePriority(sensorId, updatePriority)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Camera sensor.
updatePriority(float): The new update priority for this Camera sensor.
data = extensions.tech_sensors.processCameraData(sensorId)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Camera sensor.
Returns: data(table): The latest data from the Camera sensor, placed in seperate fields of the table.
pixel = extensions.tech_sensors.convertWorldPointToPixel(sensorId, pointInWorldSpace)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Camera sensor.
pointInWorldSpace(Point3F): A 3D point in world-space, to be converted to a pixel value on the Camera sensor.
Returns: pixel(vec3): The Camera pixel which relates to the given world-space point.
The following three functions can be used to send ad-hoc polling requests to a Camera sensor. This is when we just want an occasional reading. We need to first send a request using sendCameraRequest, then wait for it. We can check it is complete using isRequestComplete (see below), then retrieve it using collectCameraRequest.
requestId = extensions.tech_sensors.sendCameraRequest(sensorId)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Camera sensor.
Returns: The unique Id number of the ad-hoc sensor polling request which is being sent.
isComplete = extensions.tech_sensors.isRequestComplete(requestId)
Args:
requestId(int): The ID number of the ad-hoc sensor polling request to check on.
Returns: isComplete(bool): True if the ad-hoc polling request has been completed, otherwise false.
data = extensions.tech_sensors.collectCameraRequest(requestId)
Args:
requestId(int): The ID number of the ad-hoc sensor polling request.
Returns: data(table): The Camera readings.
extensions.tech_sensors.removeSensor(sensorId)
Args:
sensorId(int): The ID number of the Lidar sensor to remove.
Returns: nil.
Example for the camera use at the Lua console.
sensorId = extensions.tech_sensors.createCamera(vehicleId, {pos=vec3(0.0,2.0,1.5),size={1280,720},fov=60,renderInstance=false})
Annotations
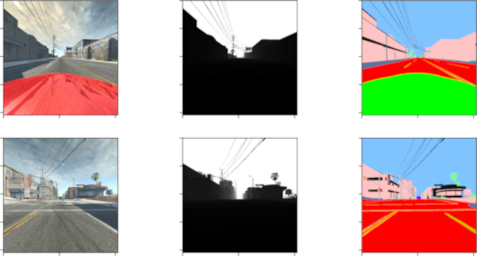
The result of a camera’s render includes additional ground truth information beyond the typical color data traditionally captured by cameras. For each render, the camera can also provide pixel-perfect annotations that encode the class of an object a pixel belongs to. This data is written to the given annotationShmem when using createCameraWithSharedMemory or into the annotation entry in the table of createCamera. Annotation classes can be seen/configured in the annotations.json file found in BeamNG.tech’s installation folder. An example pair of color and semantic annotation information looks like this; each pixel in the left image corresponds to a pixel encoding the type of the object that produced the pixel in the right image:
Annotation information is included by default when using createCamera and can be found in the annotation entry of the resulting table. When using createCameraWithSharedMemory, the data is written to the annotationShmem iff provided.
Depth Information
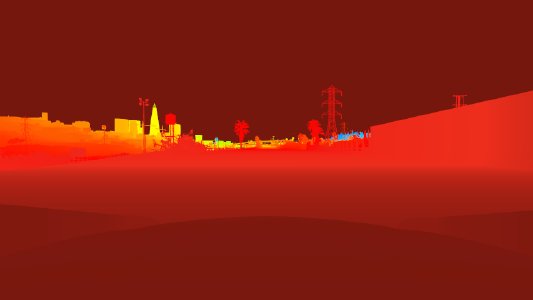
Cameras can also be used to extract depth information from the perspective of the camera. In this case, an additional image of floats is returned where each pixel contains the distance of the point that produced the pixel to the camera. One example looks like this, taken at the toll booth on West Coast USA:
Depth information is included by default when using createCamera and can be found in the depth entry of the resulting table. When using createCameraWithSharedMemory, the data is written to the depthShmem iff provided.
Was this article helpful?