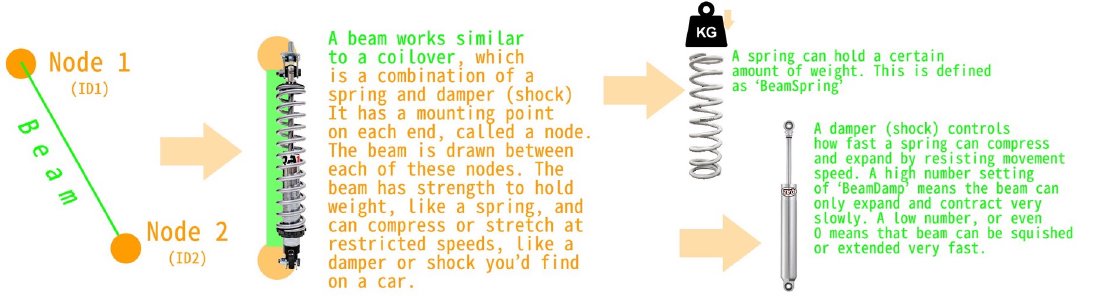
Beams
Where BeamNG gets its name - beams.
These are the spring/damper connections between nodes, and serve to build the main structure of any vehicle in the game, allowing for deformation and breakages as required.
There are multiple types of beams for all sorts of purposes, which you can see in more detail in the various examples. Standard beams act as simple springs with damping, with the ability to deform and break if needed, and are used for most applications.
All arguments that apply to standard beams can be used with each of the specialized beam types.
Required arguments
Optional arguments
The Beams section has many optional arguments. We will divide them into categories, which will be sorted from most to least frequently used.
General
These are the most basic arguments, used everywhere in Jbeam files, necessary for correct simulation. Check the introduction page for a simple explanation.
Possible values:
- NORMAL - General use beams, don’t have any special properties, used in most structures.
- SUPPORT - The second most used type of beams. These only resist forces in compression, not in extension. With precompression, they start resisting forces when reaching the precompressed length. They can automatically break when reaching a set length. Usually used when multiple parts are connected together - they don’t serve as attachments for those parts, but as limiters, preventing the nodes of one part to clip inside the surface of the other.
- HYDRO - Defined in a separate section but sharing all normal beam properties, hydros can change length on demand, usually used for steering racks. They can also define the steering wheel lock angle of the car.
- ANISOTROPIC - They have separate beamSpring and beamDamp values for expansion than for compression, can define transition zone between the two behavior variants, and can also automatically break when exceeding a certain length ratio. Used to simulate structures that are stiffer in expansion than in compression, such as tires (where they are automatically generated), ropes or soft tops.
- BOUNDED - More complicated than anisotropic beams, these can have different beamSpring and beamDamp values not just for compression and extension, but also for low and high compression and extension speed. The contraction and expansion can be defined as a ratio or metric range, and the transition zone can be modified. They are computationally expensive to use and should usually only be used in suspension components such as dampers and bump stops.
- LBEAM - Defined with 3 node IDs instead of 2, they resist angle change between 2 beams created between those nodes, rather than a distance between 2 nodes. They can provide high lateral stiffness with low compression resistance. They are used for tires (where they are auto generated) and leaf springs.
- PRESSURED - Special beams used to simulate air cylinders. Their forces are inversely proportional to their real time length. You can set the starting pressure in Pa or PSI, maximum pressure above which the beam breaks, surface of the cylinder and its volume coefficient. Used in tires (auto generated) and progressive air springs.
- BROKEN - Broken beams stop resisting forces. You cannot set this type by typing it in Jbeam.
Force required to change the length of the beam by a set amount. Excessively high stiffness compared to node weight can cause the beam to vibrate and cause instability issues.
A beam with the beamSpring value of 0 will not be shown in the console as a duplicate. This allows for adding extra damping beams in the structure.
How much force the beam can resist before breaking.
A value of “FLT_MAX” will result in an unbreakable beam.
Breakable
Used only on breakable beams, ones with beamStrength other than “FLT_MAX”. These kind of beams are used to simulate plastic, or to attach various components of a vehicle together.
When the argument is a string, the beam belongs to a single specified breakGroup. This is the usual case.
["a","b", {"breakGroup":"group_1"}],
When the argument is a table, the beam belongs to all the specified breakGroups. It means it gets automatically broken when any beam in any of these breakGroups breaks, and it triggers breakGroup breaking in both groups too. This is very rarely used in practice, and is not supported by the beam visualization debug modes.
["a","b", {"breakGroup":["group_1","group_2"]}],
Mesh breaking allows polygons of a flexbody mesh to be dynamically removed when an underlying beam breaks. This can be used to avoid excessive stretching of meshes when part of its assigned jbeam structure breaks free.
Disabling mesh breaking is useful when the breakable beam only acts as a structural support, for example in passenger cabins.
Triangle breaking allows the vehicle’s triangles to be dynamically transitioned to a state without collision and aero when an underlying beam breaks. This is used when a triangle connects 2 components that can break apart, such as a vehicle body and frame, and in case of breakable glass, in order to dynamically make a physical hole in it.
Disabling triangle breaking is useful when the breakable beam only acts as a structural support, for example in passenger cabins.
This is used for cases where one of the nodes that make up the beam is located in an optional component.
It will also hide warnings related to duplicate beams.
Deformation limiters
Used to limit a beam’s deformation. DeformLimitExpansion is the most frequently used of these, used in most Jbeam files.
Deform groups
Deform groups are used to trigger an action when a beam deforms. Most often used only for visual glass/lights damage and powertrain damage.
Used to trigger flexbody deform groups. Is also used for damage simulation on some powertrain components.
When the argument is a string, the beam belongs to a single specified deformGroup. This is the usual case.
["a","b", {"deformGroup":"group_1"}],
When the argument is a table, the beam belongs to all the specified deformGroups. It means that it triggers multiple deform behaviors at once. This is very rarely used in practice, and is not supported by the beam visualization debug modes.
["a","b", {"deformGroup":["group_1","group_2"]}],
A beam with a deformGroup will not be treated as a duplicate beam by the console. This is due to a common case of using brittle duplicate beams to simulate breakable glass.
If a beam has both a breakGroup and a deformGroup, breaking it will spawn glass or wood particles depending on the nodeMaterial of both of its nodes. This is used for vehicle windows and wooden props like the piano.
Typical values are very small numbers under 0.1. If the beam is shortened or lengthened by more than that amount, the deformGroup will be triggered.
The existence of this property on a beam will create a deform trigger for the beam, causing extra code to be executed whenever any beam with this property is deformed. This can be performance intensive, so it should only be used where it’s needed.
Precompression
These arguments define a length change of the beam on spawn. They are most often used in suspension components.
Overrides beamPrecompression.
A value of 0.2 would cause the beam to lengthen by 0.2 meters on spawn, while a value of -0.2 would cause the beam to shorten by 0.2 meters on spawn.
Drivetrain and suspension
Used only on certain suspension components and other critical vehicle parts.
Only applies to normal, bounded, and l-beams.
Used mostly with suspension components and other critical parts of the jbeam to help run higher damping before instability kicks in.
Expensive to run, should only be used where needed.
Suspension sounds
These arguments are used on beams that work the roles of struts or shock absorbers in a vehicle. They should all be used together in line only on those beams.
Cargo
Used only on cargo loads.
Example usage:
{"beamSpringFunction":"=150*$load+1100","cargoGroup":"RoofbarTank1"},
Example usage:
{"beamDampFunction":"=0.2*$load+50","cargoGroup":"RoofbarTank1"},
Example usage:
{"beamStrengthFunction":"=150*$load+1100","cargoGroup":"RoofbarTank1"},
Example usage:
{"beamDeformFunction":"=150*$load+1100","cargoGroup":"RoofbarTank1"},
Debug
These are for short term debug purposes and should be removed in the final version of the structure.
The table consists of 3 elements, including 2 required ones and 1 optional: “radius” is a number that sets the highlight radius in meters and “col” is either a string with the hex value of the color, or a table with RGB values. Example usage:
["a","b", {
"highlight":{
"radius":0.005,
"col":"#ff0000ff"
}
}],
This will produce the same effect:
["a","b", {
"highlight":{
"radius":0.005,
"col":{
"r":255,
"g":0,
"b":0,
"a":255
}
}
}],
“length” is an optional argument which will overwrite the length of the cylinder highlighting the beam with the provided value in meters. It can be longer or shorter than the default length of the beam. The center of the cylinder will always be in the center of the beam. This argument is available as of BeamNG version 0.34 and later.
["a","b", {
"highlight":{
"radius":0.005,
"col":"#ff0000ff",
"length":0.1
}
}],
Simple Example
A beam between nodes a and b
"beams": [
["id1:", "id2:"],
["a","b"],
]
Advanced Example
Example of a typical beam section, which begins by initializing all the properties that will be used for the following beams.
{
"beams": [
["id1:", "id2:"],
//--BODYWORK--
//roof main shape lengthwise
{"beamPrecompression":1, "beamType":"|NORMAL", "beamLongBound":1, "beamShortBound":1},
{"beamSpring":1401000,"beamDamp":140},
{"beamDeform":32700,"beamStrength":"FLT_MAX"},
{"deformLimitExpansion":1.1},
["rf1r","rf2r"],
["rf1","rf2"],
["rf1l","rf2l"],
["rf2r","rf3r"],
["rf2","rf3"],
["rf2l","rf3l"],
["rf3r","rf4r"],
["rf3","rf4"],
["rf3l","rf4l"],
]
}
0.37.5.0 contains
814179 entries in
10859 sections distributed over
19809 parts in
5047 jbeam files.Was this article helpful?