Torsionbars
This feature is supported as of BeamNG.tech and .drive version 0.14.0 to latest.
Torsion bars are used when you want to have a certain amount of resistance to torque between two levers. They are defined using 4 nodes, which define the end of the first lever, the two nodes that serve as the axis, and the end of second lever.
They are used to simulate structures that resist forces in torsion like sway bars, and to help rigidify flat structures like ladder chassis and shock mounts of suspension arms without the use of rigidifier nodes.
If a beam located between 2 consecutive nodes of a torsion bar breaks, the torsion bar itself will break.
The angle between the axis and the lever should be as close as possible to 90 degrees. The further away it is, the less stable the torsionbar (higher risk of Jbeam instability). Therefore you should choose the nodes for the levers carefully.
Anisotropic Torsionbars
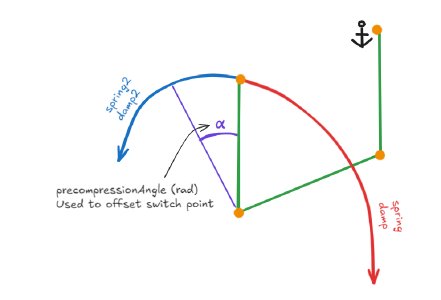
Anisotropic torsionbars are the torsionbar equivalent of anisotropic beams (the beams with varying stiffness and damping values between compression and expansion). These torsionbars resist torque differently depending in which direction the lever has twisted. Imagining one of the levers as fixed in 3D space might help you visualize this. Twisting one of the levers is the same as twisting the other in the opposite direction.
A torsionbar becomes an anisotropic torsionbar once the spring2 and/or damp2 values are defined. Depending on which way the lever has twisted depending to the starting point, the torsionbar will use either spring and damp, or spring2 and damp2 values to resist torque. Precompression angle will offset the starting point like it normally offsets the spawn angle. This is useful for making a torsionbar equivalent of a support beam - setting spring and damp to 0 and using precompressionAngle to set the angle at which the torsionbar will start resisting torque using spring2 and damp2.
Required arguments
Optional arguments
Simple Example
Standard torsion bars
"torsionbars": [
["id1:", "id2:", "id3:", "id4:"],
{"spring":10000000, "damp":100, "deform":25000, "strength":100000},
//rigidify steering arm
["oma1tl", "oma1l", "oma1r", "omatiltr"],
["oma1tr", "oma1r", "oma1l", "omatiltl"],
],
Advanced Example
Anisotropic torsion bars
"torsionbars": [
["id1:", "id2:", "id3:", "id4:"],
//steering limiters
{"deform":25000, "strength":125000},
["fh3r","fax2r","fax1r","fax3r",{"precompressionAngle":0.75,"precompressionTime":0,"spring":200000,"damp":1,"spring2":0,"damp2":0}],
["fh3r","fax1r","fax2r","fax3r",{"precompressionAngle":1.05,"precompressionTime":0,"spring":200000,"damp":1,"spring2":0,"damp2":0}],
["fh3l","fax1l","fax2l","fax3l",{"precompressionAngle":0.75,"precompressionTime":0,"spring":200000,"damp":1,"spring2":0,"damp2":0}],
["fh3l","fax2l","fax1l","fax3l",{"precompressionAngle":1.05,"precompressionTime":0,"spring":200000,"damp":1,"spring2":0,"damp2":0}],
],
Was this article helpful?